How Long Can You Live with Blocked Arteries?

How Long Can You Live with Blocked Arteries? Blocked arteries, also known as arterial blockages, refer to the narrowing or complete blockage of blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to different parts of the body. This medical condition can occur due to various factors, including atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, and family history. While blocked arteries can affect anyone, they are more prevalent among older individuals and those with unhealthy lifestyle habits. Understanding the causes, symptoms, complications, and treatment options for blocked arteries is critical to managing this condition and reducing the risk of life-threatening events, such as heart attacks and strokes.
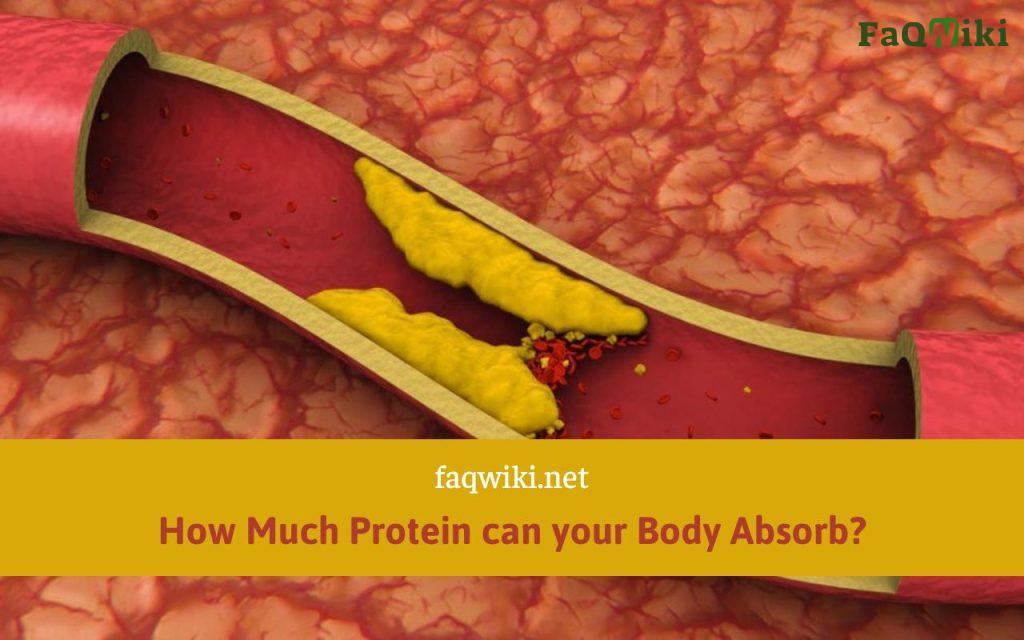
Causes of Blocked Arteries
Atherosclerosis is the most common cause of blocked arteries. It is a chronic inflammatory disease that occurs when fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances build up inside the artery walls, forming plaques. Over time, these plaques can harden and narrow the arteries, reducing blood flow and causing various health problems. Other factors that can contribute to blocked arteries include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, and family history. High blood pressure can cause the arteries to narrow and weaken, while high cholesterol levels can lead to the formation of plaques. Diabetes can also damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of atherosclerosis. Smoking, on the other hand, can damage the lining of the arteries and trigger the formation of plaques. Finally, family history can increase the risk of developing blocked arteries, as some people may inherit genes that make them more susceptible to this condition.
Symptoms of Blocked Arteries
The symptoms of blocked arteries can vary depending on the location and severity of the blockage. For some, they may not exhibit any indications whatsoever while others could have gentle to extreme symptoms. Chest pain or angina is one of the most common symptoms of blocked arteries. It occurs when the heart muscle does not receive enough oxygenated blood, causing a tight or squeezing sensation in the chest. Shortness of breath is another symptom that can occur when the lungs do not receive enough oxygenated blood. Fatigue, dizziness, nausea, and sweating are also common symptoms of blocked arteries. These symptoms may occur during physical activity or at rest and can be accompanied by palpitations or irregular heartbeat.
Complications of Blocked Arteries
Blocked arteries can lead to various complications, including heart attacks, strokes, peripheral artery disease, kidney disease, and erectile dysfunction. A heart attack occurs when the blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked, causing the heart muscle to die. Strokes occur when the blood flow to the brain is interrupted, leading to brain damage. Peripheral artery disease occurs when the blood flow to the legs and arms is reduced, causing pain, numbness, and tingling. Kidney disease can occur when the blood flow to the kidneys is reduced, leading to kidney failure. Erectile dysfunction can occur when the blood flow to the penis is reduced, making it difficult to achieve or maintain an erection.
Diagnosis of Blocked Arteries
Diagnosing blocked arteries usually involves a combination of physical examination, blood tests, imaging tests, coronary angiography, and cardiac catheterization. During a physical examination, a healthcare provider may check for signs of reduced blood flow, such as weak or absent pulses, and listen for abnormal heart sounds. Blood tests can be used to measure cholesterol levels, blood sugar levels, and other markers of inflammation and heart disease. Imaging tests, such as echocardiography, computed tomography (CT) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, can be used to visualize the heart and blood vessels and detect any abnormalities. Coronary angiography and cardiac catheterization involve the insertion of a thin, flexible tube into a blood vessel in the arm or leg and threading it up to the heart. This allows the healthcare provider to inject a contrast dye and take X-ray images of the coronary arteries to determine the location and severity of any blockages.
Treatment of Blocked Arteries
The treatment options for blocked arteries depend on the location and severity of the blockage, as well as the individual’s overall health and medical history. Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and following a balanced diet, can help reduce the risk of further blockages and improve overall heart health. Medications, such as cholesterol-lowering drugs, blood pressure medications, and blood thinners, can also be prescribed to manage the symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. In some cases, surgical procedures, such as angioplasty and stenting or bypass surgery, may be necessary to remove the blockages or redirect blood flow.
Living with Blocked Arteries
Living with blocked arteries requires a commitment to maintaining a healthy lifestyle, taking medications as prescribed, and attending regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers. Individuals with blocked arteries should also be aware of the warning signs of heart attacks and strokes, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and weakness on one side of the body, and seek medical attention immediately if these symptoms occur. In addition, they should avoid smoking, limit alcohol intake, manage stress, and follow a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
Read more here: https://faqwiki.net/
FAQs
Q: Can blocked arteries be reversed?
A: While it is not possible to reverse the damage caused by blocked arteries completely, lifestyle changes, medications, and surgical procedures can help manage the symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
Q: Can blocked arteries cause sudden death?
A: Yes, blocked arteries can lead to sudden death if a heart attack or stroke occurs.
Q: Can blocked arteries be prevented?
A: Yes, blocked arteries can be prevented by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing underlying medical conditions, and seeking prompt medical attention for any symptoms of heart disease.
Q: What are the risk factors for blocked arteries?
A: The risk factors for blocked arteries include atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, and family history.
Q: How are blocked arteries diagnosed?
A: Blocked arteries are diagnosed using a combination of physical examination, blood tests, imaging tests, coronary angiography, and cardiac catheterization.
Summary
Blocked arteries are a common medical condition that can lead to serious complications, such as heart attacks and strokes. Understanding the causes, symptoms, complications, and treatment options for blocked arteries is critical to managing this condition and reducing the risk of life-threatening events. Lifestyle changes, medications, and surgical procedures can help manage the symptoms and reduce the risk of complications associated with blocked arteries. Individuals with blocked arteries should also be aware of the warning signs of heart attacks and strokes and seek medical attention immediately if these symptoms occur.
