What Does a PCOS Belly Look Like? Understanding the Symptoms and Causes

Introduction
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder affecting 5-10% of reproductive-aged women. This endocrine disorder is a universal problem among women who are at their reproductive peak. PCOS is a complex condition, with many different symptoms and manifestations. One of the most visible symptoms is a PCOS belly, which is a characteristic appearance of fat accumulation around the waist and abdomen. In this article, we will discuss the symptoms and causes of PCOS belly fat and provide tips for prevention and management.
Understanding PCOS
PCOS is a hormonal imbalance that disrupts the normal functioning of the ovaries. It is characterized by the presence of multiple cysts on the ovaries, which interfere with ovulation and the menstrual cycle. Although the precise origins of PCOS remain unclear, researchers believe that it may be due to a combination of hereditary and environmental influences. Insulin resistance, hormonal imbalances, and inflammation may also play a role in the development of PCOS.
Symptoms of PCOS
PCOS can cause a range of symptoms, including physical, emotional, and behavioral symptoms. Physical symptoms may include irregular menstrual cycles, acne, excess hair growth, and weight gain, especially in the abdominal area. Emotional symptoms may include anxiety, depression, and mood swings. Behavioral symptoms may include sleep disturbances, decreased sex drive, and difficulty losing weight.
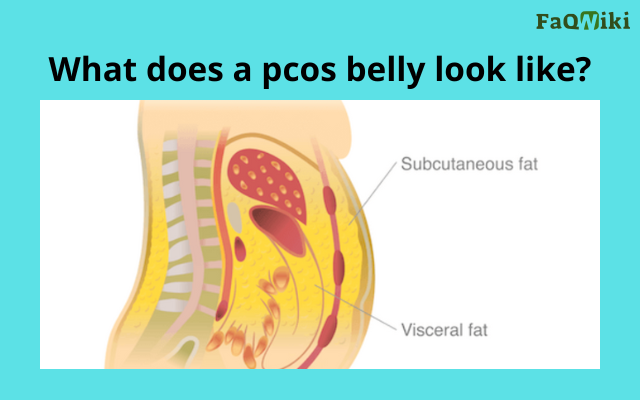
PCOS and Belly Fat
PCOS is frequently characterized by the accumulation of pesky belly fat. Women with PCOS tend to accumulate fat in the abdominal area, which can lead to a characteristic “apple” shape. This type of fat distribution is associated with an increased risk of diabetes, heart disease, and other health problems. PCOS belly fat is also associated with insulin resistance, a condition in which the body’s cells become resistant to insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels.
PCOS Belly: Appearance and Characteristics
A PCOS belly is characterized by a thick layer of fat around the waist and abdomen. This fat is often firm to the touch and may have a lumpy or dimpled appearance. The waist may be disproportionately larger than the hips and thighs, creating an “apple” shape. Women with PCOS may also experience bloating and digestive issues, which can contribute to the appearance of a PCOS belly.
Causes of PCOS Belly Fat
The exact causes of PCOS belly fat are not well understood, but several factors may contribute to its development. Insulin resistance is one of the most common causes of PCOS belly fat. Women with PCOS have higher levels of insulin than normal, which can lead to increased fat storage in the abdominal area. Hormonal imbalances, such as high levels of androgens (male hormones), may also contribute to the development of PCOS belly fat. Lifestyle factors, such as a sedentary lifestyle and a diet high in refined carbohydrates and sugar, may also contribute to the development of PCOS belly fat.
How to Identify PCOS Belly Fat
PCOS belly fat can be identified by measuring waist circumference and looking at the distribution of fat around the abdomen. A waist circumference of 35 inches or more in women indicates an increased risk of health problems associated with abdominal obesity, such as diabetes and heart disease. Women with PCOS may also have a characteristic “apple” shape, with a larger waist circumference than hip circumference.
Treatment and Management of PCOS Belly Fat
Treatment and management of PCOS belly fat may involve a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and surgery. Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise and a healthy diet, can help reduce belly fat and improve insulin resistance. Medications, such as metformin and birth control pills, may also be prescribed to help
control hormonal imbalances and improve insulin sensitivity. In some cases, surgery such as liposuction may be used to remove excess fat from the abdomen.
Prevention of PCOS Belly Fat
Prevention of PCOS belly fat involves making healthy lifestyle choices. Eating a diet that is low in refined carbohydrates and sugar and high in fiber and protein can help reduce belly fat and improve insulin sensitivity. Regular exercise can also help reduce belly fat and improve overall health. Stress reduction techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can also be helpful in reducing the risk of PCOS belly fat.
Understanding the Link between PCOS and Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is a key factor in the development of PCOS and PCOS belly fat. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps the body to use glucose (sugar) for energy. When insulin resistance develops in the body, the pancreas responds by secreting additional amounts of insulin to keep up. This can lead to high levels of insulin in the blood, which can cause the body to store fat, especially in the abdominal area.
Tips for Managing Insulin Resistance in PCOS
Managing insulin resistance is an important part of preventing and managing PCOS belly fat. Some tips for managing insulin resistance in PCOS include eating a diet that is low in refined carbohydrates and sugar and high in fiber and protein, engaging in regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight. Medications such as metformin may also be prescribed to help manage insulin resistance in PCOS.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve PCOS Belly Fat
Making lifestyle changes can be an effective way to improve PCOS belly fat. Rewriting your lifestyle to experience optimal health may include the following habits:
Eating a Healthy Diet
Eating a healthy diet that is low in refined carbohydrates and sugar and high in fiber and protein can help reduce belly fat and improve insulin sensitivity.
Engaging in Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular exercise can help reduce belly fat and improve overall health. Strive to engage in at least 30 minutes of moderate physical activity on a daily basis for optimal health.
Reducing Stress
Stress can contribute to the development of PCOS belly fat. Incorporating yoga, meditation and deep breathing can be a useful way to reduce stress levels and still maintain optimum health.
Getting Enough Sleep
Getting enough sleep is important for overall health and can also help reduce stress and improve insulin sensitivity.
Avoiding Smoking and Alcohol
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to the development of PCOS belly fat and other health problems. Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption can help reduce the risk of PCOS belly fat.
Conclusion
PCOS belly fat is a common symptom of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Women with PCOS tend to accumulate fat in the abdominal area, which can lead to an increased risk of health problems. Understanding the causes and symptoms of PCOS belly fat is important for prevention and management. Making healthy lifestyle choices, managing insulin resistance, and seeking medical treatment when necessary can help reduce the risk of PCOS belly fat and improve overall health.
FAQs
Can PCOS belly fat be reversed?
PCOS belly fat can be managed and reduced with lifestyle changes, medication, and surgery if necessary. However, it may not be completely reversible in all cases.
Is PCOS belly fat dangerous?
PCOS belly fat is associated with an increased risk of health problems such as diabetes and heart disease. However, with proper management and treatment, the risk can be reduced.
Can losing weight reduce PCOS belly fat?
Losing weight can help reduce PCOS belly fat and improve insulin sensitivity. However, weight loss can be difficult for women with PCOS, and it is important to work with a healthcare professional to develop a safe and effective weight loss plan.