Why Do My Eyes Hurt When I Look Around?

Have you ever experienced eye pain when looking around? It’s a common phenomenon that many people face, and it can be quite uncomfortable. Eye pain can range from mild discomfort to severe pain and can be caused by various factors. In this article, we’ll explore the reasons why your eyes may hurt when you look around, the importance of addressing the issue, and ways to prevent and treat eye pain. So, whether you’re someone who experiences occasional eye pain or someone who suffers from chronic eye pain, this article is for you.
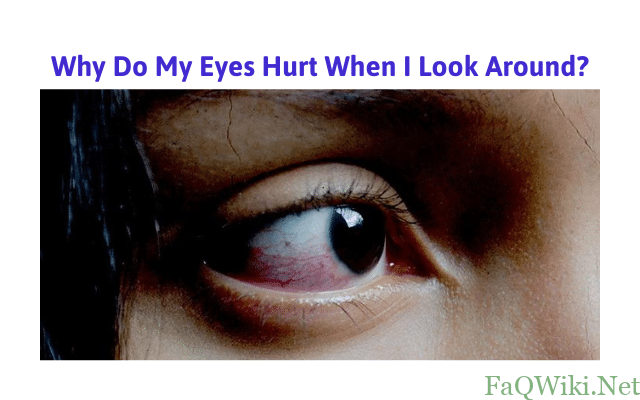
Anatomy of the Eye
The eye is a complex organ that allows us to see the world around us. It consists of several parts, each with a unique function.
Structure of the Eye
The eye has three layers: the outer layer, the middle layer, and the inner layer. The outer layer consists of the cornea and the sclera, which are the clear, protective covering and the white part of the eye, respectively. The middle layer contains the iris, the pupil, and the ciliary body. The iris is the colored part of the eye that controls the amount of light that enters the eye, while the pupil is the black hole in the center of the iris that allows light to enter the eye. The ciliary body is a muscle that controls the shape of the lens. The inner layer contains the retina, which is a layer of cells that receive and process light.
Function of Each Part of the Eye
Each part of the eye has a specific function. The cornea and the lens focus light onto the retina, which contains cells called photoreceptors that convert the light into electrical signals that are sent to the brain. The iris and the pupil regulate the amount of light that enters the eye, while the ciliary body controls the shape of the lens, which allows us to see objects at different distances.
Explanation of How the Eye Works
When light enters the eye, it is focused by the cornea and the lens onto the retina. The photoreceptor cells in the retina convert the light into electrical signals that are sent to the brain through the optic nerve. The brain then interprets these signals and creates the images that we see. The process of focusing the light onto the retina is called refraction, and it is crucial for clear vision. Any abnormalities in the structure or function of the eye can cause vision problems and, in some cases, eye pain.
Common Causes of Eye Pain
Eye pain can be caused by various factors. Some of the most common causes of eye pain include:
Eye Strain
Definition of Eye Strain
Eye strain, also known as asthenopia, is a condition that occurs when your eyes become tired from prolonged use, such as staring at a computer screen or reading for an extended period.
Symptoms of Eye Strain
Symptoms of eye strain include:
- Sore, tired, or burning eyes
- Headache
- Blurred or double vision
- Dry eyes
- Neck or shoulder pain
Causes of Eye Strain
Eye strain can be caused by several factors, including:
- Prolonged use of digital devices
- Reading in dim light
- Driving long distances
- Poor posture
- Stress
Dry Eyes
Definition of Dry Eyes
Dry eyes occur when your eyes do not produce enough tears, or the tears evaporate too quickly.
Symptoms of Dry Eyes
Symptoms of dry eyes include:
- Burning, stinging, or itching eyes
- Redness
- Sensitivity to light
- Blurred vision
- Eye fatigue
- Stringy mucus in or around the eyes
Causes of Dry Eyes
Dry eyes can be caused by several factors, including:
- Aging
- Certain medications
- Medical conditions such as Sjogren’s syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus
- Environmental factors such as wind, smoke, and dry air
Eye Infections
Definition of Eye Infections
Eye infections occur when harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria or viruses, invade the eye.
Symptoms of Eye Infections
Symptoms of eye infections include:
- Redness
- Pain
- Discharge
- Blurred vision
- Sensitivity to light
- Swelling of the eyelids
Causes of Eye Infections
Eye infections can be caused by several factors, including:
- Bacteria
- Viruses
- Fungi
- Parasites
Allergies
Definition of Allergies
Allergies occur when your immune system overreacts to a harmless substance, such as pollen, dust, or pet dander.
Symptoms of Allergies
Symptoms of allergies include:
- Red, itchy, or watery eyes
- Sneezing
- Runny nose
- Itchy throat
- Skin rash or hives
Causes of Allergies
Allergies can be caused by several factors, including:
- Pollen
- Dust
- Pet dander
- Mold
- Certain foods
Migraines
Definition of Migraines
Migraines are a type of headache that typically causes a severe throbbing pain on one side of the head.
Symptoms of Migraines
Symptoms of migraines include:
- Throbbing pain on one side of the head
- Sensitivity to light and sound
- Nausea or vomiting
- Blurred vision
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
Causes of Migraines
The exact cause of migraines is unknown, but they are thought to be caused by changes in the brain and genetics. Certain triggers, such as stress, lack of sleep, and certain foods, can also cause migraines.
When to See an Eye Doctor
Eye pain can be a sign of a serious underlying condition. It is important to seek professional help if you experience eye pain that does not go away on its own or if you experience any other concerning symptoms. An eye doctor, also known as an optometrist or ophthalmologist, can help diagnose and treat the underlying cause of your eye pain.
Importance of Seeking Professional Help
Seeking professional help is important for several reasons:
- An eye doctor can diagnose and treat the underlying cause of your eye pain.
- Delaying treatment can lead to permanent damage to your eyesight.
- Some eye conditions, such as glaucoma and macular degeneration, have no early symptoms, making regular eye exams crucial.
When to See an Eye Doctor
You should see an eye doctor if you experience any of the following:
- Eye pain that does not go away
- Blurred or double vision
- Redness or swelling of the eye
- Sensitivity to light
- Eye discharge
- Changes in your vision, such as loss of vision or sudden flashes of light
What to Expect During a Visit
During your visit to an eye doctor, they will likely perform a comprehensive eye exam, which may include the following:
- An evaluation of your vision
- A measurement of your eye pressure
- A dilated eye exam to examine the inside of your eye
- Additional tests, such as a visual field test or a retinal exam, may also be performed if necessary.
Based on the results of your exam, your eye doctor may prescribe medication or recommend other treatments, such as eye drops, surgery, or lifestyle changes. It is important to follow their recommendations closely to ensure the best possible outcome for your eye health.
Preventing Eye Pain
Eye pain can often be prevented by taking care of your eyes and making small changes to your daily routine. Here are some tips for preventing eye pain:
Proper Lighting
Proper lighting is essential to prevent eye strain. Make sure that the lighting in your home or workplace is adequate for the tasks you are performing. Avoid working in areas that are too dimly lit or too bright.
Adjusting Computer Screens
Staring at a computer screen for extended periods can cause eye strain. Adjust your computer screen so that it is at the appropriate height and distance from your eyes. You can also adjust the brightness and contrast levels of your screen to make it more comfortable to use.
Taking Breaks
Taking frequent breaks can help prevent eye strain. Follow the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look away from your computer screen and focus on an object that is at least 20 feet away for 20 seconds.
Wearing Sunglasses
Protecting your eyes from the sun’s harmful UV rays can prevent eye strain and damage to your eyes. Wear sunglasses that block at least 99% of UV rays when you are outside.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can also help prevent eye pain. Make sure to eat a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, exercise regularly, and get enough sleep.
Eye Exercises
Eye exercises can help improve eye muscle strength, reduce eye strain, and prevent eye pain. Here are some types of eye exercises:
- Blinking: Blinking rapidly for a few seconds can help refresh your eyes and reduce eye strain.
- Eye massage: Gently massaging your eyelids can help stimulate blood flow to your eyes and reduce eye strain.
- Eye rotations: Rotating your eyes in a circular motion can help improve eye muscle strength and flexibility.
- Focusing: Focusing on objects at different distances can help improve your eye’s ability to change focus quickly and reduce eye strain.
Incorporating these tips into your daily routine can help prevent eye pain and maintain good eye health.
Treating Eye Pain
If you are experiencing eye pain, there are various treatments available depending on the cause of the pain. Here are some common treatments for eye pain:
Over-the-Counter Remedies
Over-the-counter remedies can help alleviate mild eye pain caused by allergies, dry eyes, or eye strain. These remedies may include lubricating eye drops, antihistamine eye drops, or pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
Eye Drops
Eye drops are a common treatment for dry eyes and other conditions that cause eye pain. Depending on the cause of the pain, your doctor may prescribe eye drops that contain lubricants, steroids, or antibiotics.
Warm Compresses
Applying a warm compress to your eyes can help relieve pain caused by styes, infections, or dry eyes. The warmth can help increase blood flow to the affected area and promote healing.
Prescription Medications
In some cases, prescription medications may be necessary to treat eye pain. These may include:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: These drugs can help reduce inflammation and pain caused by conditions such as uveitis or scleritis.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat bacterial infections such as conjunctivitis or corneal ulcers.
- Allergy medications: These drugs can help relieve eye pain caused by allergies.
Surgery
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat eye pain that is caused by a structural problem or injury. Here are some types of eye surgeries:
- Cataract surgery: This surgery involves removing the cloudy lens in your eye and replacing it with an artificial lens.
- Corneal transplant: This surgery involves replacing a damaged or diseased cornea with a healthy one from a donor.
- Glaucoma surgery: This surgery can help lower eye pressure and prevent further damage to the optic nerve.
Before undergoing any type of eye surgery, it’s important to discuss the risks and benefits with your doctor. Possible risks of eye surgery may include infection, bleeding, or vision loss.
In conclusion, if you experience eye pain, there are various treatments available depending on the cause of the pain. Over-the-counter remedies, eye drops, warm compresses, prescription medications, and surgery are all options for treating eye pain. If you are experiencing persistent or severe eye pain, it’s important to see an eye doctor for an evaluation and proper diagnosis.
Conclusion
Eye pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including eye strain, dry eyes, infections, allergies, and migraines. It’s important to understand the causes of eye pain and how to prevent it.
Preventative measures include adjusting lighting, taking breaks, wearing sunglasses, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and doing eye exercises. If you experience persistent or severe eye pain, it’s important to see an eye doctor for an evaluation and proper diagnosis.
Treatment options for eye pain include over-the-counter remedies, eye drops, warm compresses, prescription medications, and surgery. The type of treatment depends on the cause of the pain.
It’s important to address eye pain and seek professional help if necessary. Neglecting eye pain can lead to further damage and even vision loss.
By taking preventative measures and seeking treatment when needed, you can help alleviate eye pain and maintain healthy vision.
Remember to prioritize your eye health and seek help from a qualified eye care professional if you have any concerns or experience any discomfort.
FAQs
What is the most common cause of eye pain?
Eye strain is the most common cause of eye pain. It can be caused by activities such as reading, using a computer or watching TV for prolonged periods of time.
Can eye pain be a sign of something serious?
Yes, eye pain can be a sign of something serious. Eye pain can be a symptom of various conditions such as infections, inflammation, and even tumors. It’s important to seek professional help if you experience persistent or severe eye pain.
How can I prevent eye strain?
You can prevent eye strain by adjusting lighting, taking breaks, adjusting computer screens, and doing eye exercises.
What are the symptoms of dry eyes?
The symptoms of dry eyes include stinging, burning, and redness in the eyes, as well as a feeling of grittiness or dryness in the eyes.
When should I see an eye doctor?
You should see an eye doctor if you experience persistent or severe eye pain, vision changes, or any other unusual symptoms.
Can eye pain be a symptom of a migraine?
Yes, eye pain can be a symptom of a migraine. It’s important to seek professional help if you experience migraines or any other persistent or severe symptoms.
What are some common eye exercises?
Common eye exercises include the 20-20-20 rule, focusing exercises, and eye rotations.
What are some over-the-counter remedies for eye pain?
Over-the-counter remedies for eye pain include eye drops, warm compresses, and pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
What are some prescription medications for eye pain?
Prescription medications for eye pain include anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, and allergy medications.
What are the risks of eye surgery?
The risks of eye surgery include infection, bleeding, and vision loss.
How long does it take to recover from eye surgery?
The recovery time from eye surgery varies depending on the type of surgery performed. It can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks to fully recover.
