How Many Watts Does a TV Use?
Introduction
Television (TV) has become an integral part of our lives, and it’s hard to imagine a day without it. However, as much as we enjoy watching TV, we often forget about the amount of electricity it consumes. Understanding TV wattage is crucial as it helps us make informed decisions when it comes to energy consumption. In this article, we’ll dive into the topic of how many watts a TV uses, why it’s essential to know, and how TVs consume electricity.
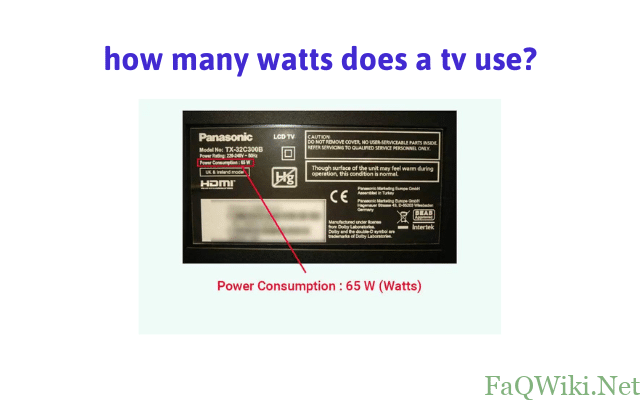
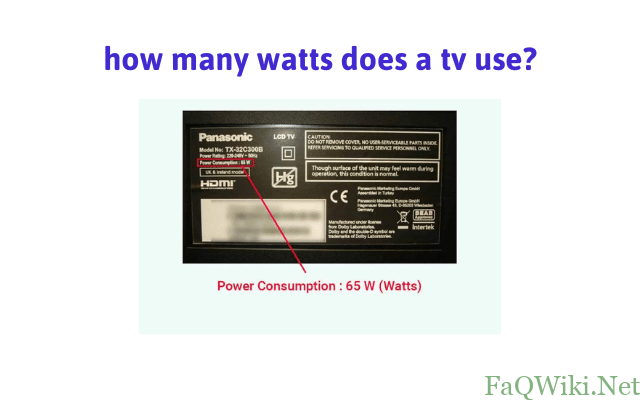
how many watts does a tv use
Understanding Watts
To understand how much electricity a TV consumes, we first need to understand the term “watt.” In simple terms, a watt is a unit of power that measures the rate at which energy is transferred or used. It’s named after James Watt, the Scottish inventor who developed the steam engine.
Watts are important because they help us understand how much power an electronic device consumes. By knowing the wattage of a TV, we can calculate its energy usage and, subsequently, its cost of operation.
In the context of electrical units, watts are commonly compared to other units such as volts, amps, and kilowatts. While volts measure the electrical potential difference, and amps measure the electrical current, watts measure the power that is being used or produced.
Watts are measured using a device called a wattmeter, which is typically used by electricians to measure the amount of power that is being used by an electrical device. The wattmeter measures both the voltage and the current in the circuit and then calculates the power (in watts) by multiplying the two values.
Factors Affecting TV Wattage
The wattage of a TV is influenced by several factors. Here are some of the most significant factors:
TV Screen Size and Type
The size and type of TV screen play a significant role in determining the wattage of a TV. Generally, larger screens consume more energy than smaller ones. Similarly, TVs with LED screens tend to be more energy-efficient than those with plasma or CRT screens.
TV Technology
The technology used in a TV also plays a significant role in determining its wattage. For example, newer TVs that use LED or OLED technology tend to be more energy-efficient than older TVs that use CRT or plasma technology.
TV Brand and Model
Different TV brands and models have varying levels of energy efficiency. Some manufacturers prioritize energy efficiency in their products, while others may not.
Brightness and Contrast Settings
The brightness and contrast settings on a TV can also affect its wattage. Higher brightness and contrast settings tend to consume more energy than lower ones.
Input Source
The type of input source used with the TV can also affect its wattage. For example, streaming content through an internet connection consumes less energy than watching content through a cable or satellite connection.
Additional Features
Additional features such as built-in sound systems, smart capabilities, and other features that require extra processing power can also increase the TV’s wattage.
TV Power Consumption Tests
Testing the power consumption of a TV can help us understand how much energy it consumes in different modes and settings. Here are some key points to know about TV power consumption tests:
Purpose of Tests
The purpose of TV power consumption tests is to measure the amount of energy consumed by a TV in different modes, such as standby mode, active mode, and different brightness and contrast settings. The tests help us understand how much energy a TV consumes and how it compares to other models and brands.
Types of Tests
There are different types of TV power consumption tests. The two primary modes tested are standby mode and active mode. Standby mode refers to the energy consumed when the TV is turned off but still plugged in. Active mode refers to the energy consumed when the TV is turned on and displaying content. Tests may also measure power consumption at different brightness and contrast settings.
How to Conduct Tests
TV power consumption tests require specialized equipment, such as a wattmeter or power analyzer, to measure the energy consumed by the TV. To conduct a test, the TV is connected to the equipment, and different modes and settings are tested. Tests may be conducted in a laboratory setting or in a home environment.
Understanding Test Results
Test results provide valuable information on how much energy a TV consumes in different modes and settings. The results may be presented in terms of wattage or energy consumption over time, such as kilowatt-hours (kWh). It’s important to compare the test results with other models and brands to understand how energy-efficient a TV is. Additionally, understanding the energy cost in your local area will help put the energy consumption in perspective.
Typical TV Wattage Ratings
Understanding the typical wattage ratings for different types of TVs can help us estimate how much energy they consume. Here are some key points to know about TV wattage ratings:
Average Wattage for Different Types of TVs
The average wattage for different types of TVs can vary significantly. Generally, LED TVs are the most energy-efficient, while plasma TVs are the least energy-efficient. Here are some average wattage ratings for different types of TVs:
- LED TVs: 50-100 watts
- LCD TVs: 80-150 watts
- OLED TVs: 100-150 watts
- Plasma TVs: 150-500 watts
Comparison of Wattage for Different TV Sizes
The wattage of a TV generally increases as the size of the screen increases. Here are some average wattage ratings for different TV sizes:
- 32-inch TV: 30-70 watts
- 42-inch TV: 55-90 watts
- 55-inch TV: 80-135 watts
- 65-inch TV: 110-180 watts
Comparison of Wattage for Different TV Brands and Models
The wattage of a TV can also vary based on the brand and model. Some manufacturers prioritize energy efficiency in their products, while others may not. Here are some average wattage ratings for different TV brands and models:
- Samsung: 60-120 watts
- LG: 50-150 watts
- Sony: 70-150 watts
- Vizio: 60-120 watts
Typical Standby Mode Wattage
TVs consume energy even when they’re turned off but still plugged in. This is called standby mode. The wattage consumed in standby mode is generally much lower than when the TV is turned on, but it can still add up over time. Here are some average standby mode wattage ratings:
- LED TVs: 0.2-1 watt
- LCD TVs: 0.5-2 watts
- OLED TVs: 0.5-2 watts
- Plasma TVs: 1-5 watts
It’s important to note that these are average ratings, and actual wattage can vary based on specific models and settings.
Factors That Can Reduce TV Wattage
Reducing TV wattage can help save energy and lower electricity bills. Here are some factors that can help reduce TV wattage:
Adjusting Brightness and Contrast Settings
Adjusting the brightness and contrast settings of a TV can significantly reduce its wattage. Brighter settings generally consume more energy than darker settings. It’s important to find the right balance between image quality and energy efficiency.
Using Power-Saving Features
Many modern TVs come with power-saving features that can help reduce wattage. These features may include automatic brightness adjustment, motion sensors that turn off the TV when no one is in the room, and standby modes that consume very little energy.
Unplugging TV When Not in Use
Unplugging the TV when not in use can help save energy and reduce wattage. TVs consume energy even when they’re turned off but still plugged in. Unplugging the TV eliminates this standby energy consumption.
Using a Power Strip
Using a power strip can help reduce wattage by allowing you to easily turn off the TV and all of its connected devices with one switch. This eliminates standby energy consumption and can save energy over time.
By implementing these factors, you can significantly reduce the wattage of your TV and save energy and money on your electricity bill.
How to Calculate TV Energy Cost
Calculating the energy cost of a TV can help you estimate how much it will cost to run it over a period of time. Here are the key factors to consider when calculating TV energy cost:
Understanding Energy Consumption Rates
Energy consumption rates for TVs are usually measured in watts per hour (Wh). To calculate the energy cost, we need to convert the wattage into kilowatt-hours (kWh), which is the unit used by utility companies to bill customers for electricity usage.
Determining Average Daily Usage
To calculate the energy cost of a TV, we first need to determine its average daily usage. This can be estimated by multiplying the number of hours per day that the TV is typically used by the wattage rating of the TV. For example, if a TV is used for 4 hours per day and has a wattage rating of 100 watts, its daily energy consumption rate would be 400 watt-hours (4 hours x 100 watts).
Calculating Yearly Energy Cost
Once we know the daily energy consumption rate, we can calculate the yearly energy cost by multiplying the daily energy consumption rate by the number of days in a year (365). To convert the watt-hours to kilowatt-hours, we divide the total watt-hours by 1,000. Finally, we multiply the result by the cost of electricity per kilowatt-hour charged by the utility company. Here’s the formula:
Yearly Energy Cost = (Daily Energy Consumption Rate x 365 / 1000) x Cost per Kilowatt-hour
For example, if a TV has a daily energy consumption rate of 400 watt-hours, the yearly energy consumption would be:
(400 watt-hours x 365 days / 1000) = 146 kWh
If the cost per kilowatt-hour charged by the utility company is $0.15, the yearly energy cost would be:
146 kWh x $0.15/kWh = $21.90
By calculating the energy cost of your TV, you can get a better understanding of its energy consumption and adjust your usage and settings accordingly to save energy and money on your electricity bill.
Tips for Reducing TV Energy Consumption
Reducing the energy consumption of your TV not only helps you save money on your electricity bill, but it also reduces your carbon footprint. Here are some tips to help you reduce your TV’s energy consumption:
Choosing an Energy-Efficient TV
When purchasing a new TV, look for the Energy Star label. This label indicates that the TV meets strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Energy Star certified TVs use up to 30% less energy than non-certified models.
Proper TV Placement and Ventilation
Make sure your TV is placed in a well-ventilated area with enough space around it to allow for proper air circulation. This helps prevent overheating and reduces the need for the TV to use more energy to cool down. Also, avoid placing your TV near heat sources, such as radiators or direct sunlight, as this can cause the TV to use more energy to maintain a consistent temperature.
Keeping the TV Clean
A dirty TV screen can reduce brightness and image quality, which may cause you to increase the brightness settings and use more energy. Clean the TV screen and other surfaces regularly with a soft, dry cloth to remove dust and dirt.
Other Energy-Saving Habits
There are other habits you can adopt to reduce your TV’s energy consumption, such as:
- Turning off the TV when not in use: Don’t leave your TV on when you’re not actively watching it. Turning off the TV completely saves the most energy.
- Using a power strip: Plug your TV and other electronics into a power strip and turn off the power strip when not in use. This helps prevent “phantom” energy use, which occurs when devices consume energy even when they’re turned off.
- Adjusting settings: Lowering the brightness and contrast settings can reduce the TV’s energy consumption. Also, enabling power-saving features, such as automatic brightness adjustment and automatic shut-off, can help reduce energy use.
By following these tips, you can reduce your TV’s energy consumption and save money on your electricity bill.
Comparison of TV Wattage to Other Appliances
Understanding how much energy your TV uses can help you put it into perspective with other appliances and electronics in your home. Here’s a comparison of TV wattage to other common household items:
Comparison to Other Electronics
Compared to other electronics like computers, smartphones, and tablets, TVs use significantly more energy. For example, a typical 60-inch LED TV uses around 150 watts of energy, while a laptop computer uses around 50 watts and a smartphone uses around 5 watts.
Comparison to Major Appliances
In comparison to major appliances like refrigerators and air conditioners, TVs use significantly less energy. A typical 60-inch LED TV uses around 150 watts of energy, while a standard refrigerator uses around 725 watts and a window air conditioner uses around 1,200 watts.
Explanation of Why TV Wattage Matters
Understanding how much energy your TV uses is important for a few reasons. First, it can help you estimate your electricity bill and budget accordingly. Second, it can help you identify ways to reduce your energy consumption and save money. Finally, it can help you make more informed decisions when purchasing a new TV, as energy-efficient models can save you money in the long run.
By putting TV wattage into perspective with other household items, you can better understand how much energy your TV uses and how to make smarter decisions to reduce your energy consumption.
TV Wattage and the Environment
High TV wattage can have a negative impact on the environment in a few ways. First, it contributes to the overall demand for energy, which can lead to increased greenhouse gas emissions from power plants. Second, TVs contain materials like plastic and glass that can be harmful to the environment if not disposed of properly.
Importance of Reducing TV Energy Consumption
Reducing your TV’s energy consumption can have a positive impact on the environment by reducing your carbon footprint and energy usage. By choosing an energy-efficient TV, adjusting your settings, and turning off your TV when not in use, you can significantly reduce your energy consumption and save money on your electricity bill.
Explanation of How to Properly Dispose of Old TVs
When disposing of an old TV, it’s important to do so in an environmentally responsible way. Many electronics retailers and manufacturers offer recycling programs for old TVs, where the materials can be repurposed and reused. Some programs may charge a fee for recycling, while others may offer free recycling services.
It’s important to avoid throwing old TVs in the trash, as the materials can be harmful to the environment if not disposed of properly. By taking the time to recycle your old TV, you can help reduce your environmental impact and contribute to a more sustainable future.
By understanding the impact of TV wattage on the environment and taking steps to reduce your energy consumption, you can make a positive impact on the world around you.
Conclusion
Understanding TV wattage is an important part of being an environmentally conscious consumer. By knowing the wattage of your TV, you can calculate its energy consumption and make informed decisions about how to reduce your energy usage.
In this article, we covered a variety of topics related to TV wattage, including what watts are, factors that affect TV wattage, how to conduct power consumption tests, typical TV wattage ratings, and how to calculate TV energy cost. We also provided tips for reducing TV energy consumption and compared TV wattage to other appliances. Finally, we discussed the impact of TV wattage on the environment and the importance of properly disposing of old TVs.
It’s important to take action to reduce your TV’s energy consumption and make a positive impact on the environment. By choosing an energy-efficient TV, adjusting your settings, and turning off your TV when not in use, you can significantly reduce your energy usage and contribute to a more sustainable future.
We hope this article has been informative and helpful in understanding TV wattage and its impact on the environment. Remember, every small action you take can make a difference in the world around you.
FAQs
What is the difference between watts and volts?
Volts refer to the electrical potential difference between two points, while watts measure the rate at which energy is being used or produced. In simple terms, volts measure the force of the electrical current, while watts measure how much work is being done by that current.
How much electricity does a TV use when it is turned off?
Even when turned off, many TVs continue to use a small amount of electricity to power certain features such as the remote control sensor and standby mode. This is known as standby power, and can range from a few watts to several watts depending on the TV model.
How much can I save by reducing my TV’s wattage?
The amount you can save by reducing your TV’s wattage will depend on your specific TV model and usage habits. However, reducing your TV’s wattage can lead to significant energy and cost savings over time.
Can I use a voltage converter to reduce my TV’s wattage?
No, a voltage converter will not reduce your TV’s wattage. A voltage converter only changes the voltage of the electricity being supplied, and does not affect the amount of energy being used by your TV.
How do I know if my TV is energy-efficient?
You can determine if your TV is energy-efficient by looking for an Energy Star label on the TV. The Energy Star program is a government-backed program that certifies electronics and appliances as energy-efficient. TVs that have earned the Energy Star label meet strict energy efficiency guidelines set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
